History of agriculture in World
This article is severely incomplete, therefore a stub.
Be advised that its contents may still be under heavy development, and may be updated repeatedly. |
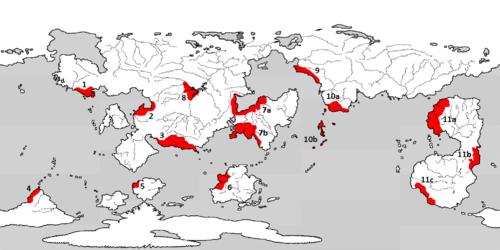
Agriculture in World began in 12 separate centres by various populations on the planet at different points in its history.
Origins
The transition from hunting-gathering to early agriculture was a direct response to the climatic changes caused by the end of the last estian ice age in 13000 BNB. At this stage, agriculture consisted of replanting wild crops, but not immediately domesticating them.
Chronological order
- South Anidon: the first truly domesticated crops appeared around 11000 BNB at agriculture centre 3, located around the anidonian coasts of the Luhanian sea. Animals such as donkeys, shéwe[1] and guineafowl had been domesticated the prior millennium, so to feed these, early southern anidonians started breeding crops like finger millet and zinzin[2] for higher yields. Eventually, these also began being used in food, and then other plants began being cultivated, such as the kenaf for its fibers, and cardamom, korarima and jasmine for flavour.
- Bahl and south Marcia: there is evidence that Bahl (centre 10a) started cultivating maygrass and amaranth early in 10500 BNB. Southern Marcia (centre 7b) began around the same time with taro, sugarcane, bananas (mainly Musa velutina), abacá, ginger, turmeric, job's tears, basil, coffee, ube, lemongrass and nutmeg.
- Arcus lake: soon after centre 3 followed centre 8, the western shores of the Arcus lake, in 10000 BNB. There, sorghum, teff, water mint, thyme, carrots and beets were first domesticated, as well as woad for the production of indigo dye, which became extensively used by the Bhymians later in history.
- Orddonach, the Gulf of the Wharm and Eluvh: in 9000 BNB, centres 1 (Eluvh), 9 (Namunia) and 7a (the shores of the Gulf of the Wharm) entered into agriculture.
- Centre 1 domesticated soybeans, adzuki, ramie, radish, rice, ma and proso millet in 9000 BNB, eggplant, spearmint, oregano, angelica, sativa hemp, parsnip, star anise, chives, eluvhian onion and foxtail millet in 8000 BNB, and peach, mandarine, watermelon, tea, coriander, myoga and cassia in 5000 BNB. Koki mold was domesticated in 400 BNB for the production of rice wine.
- Centre 7a domesticated fonio, cotton and kola nuts.
- Centre 9, one of the most well-researched areas, did wheat, rye, barley, flax, leeks, fennels, madder, oats, chickpeas, peas, lentils, olives, and bitter vetch. Later, in 8000 BNB spices and herbs became popular condiments, and so began the cultivation of cumin, licorice, celery, rosemary, summer savoury, sage and saffron, as well as the recreational poppy. In 7000 BNB, hops began being cultivated for brewing beer. Much later, anise and turnips began being domesticated in 4000 BNB.
- Although not classically considered a centre, apples began being planted independently around 9000 BNB in Phyrea.
- Bahl and north Gogg: Bahlians began cultivating bloodroot, bell peppers and bahlian mahonia in 7000 BNB. North Gogg (centre 11a) at the same time did maize, guayusa, tobacco, chia, cassava, sweet potato, old fustic, añil, achiote, açaì and lemon verbena.
- South Gogg and Luhan: 6000 BNB, centre 11c (south Gogg), tomato, yerba mate, greater walnut, and centre 6 (Luhan), kutjera.
- Central Gogg: 5000 BNB, centre 11b (central Gogg), potato, oca, common bean, peanut, cocoa.
- Cisrumpapia: centre 2 entered its agricultural era in 4000 BNB, domesticating indica hemp, garlic, cinnamon and jute.
